Classification Class
For the description how to request a new classification class, please see: Classification Class (Create Change Request).
ECLASS is a system for classification and product description. For ECLASS as a classification system, the most fundamental structural element is the classification class. With the help of classification classes products are devided into certain categories of similar products, the product groups. ECLASS is a monohierarchical classification system, i.e. every product group is to be found only once in the hierarchical tree structure. Every classification class has a unique identifier (IRDI), a preferred name and a coded name that represents the classification structure (see below). With the development of ECLASS 7.1, the definition of a classification class was defined as a mandatory field, i.e. starting with ECLASS 7.1 every new classification class has to have a definition. That does not imply that all classification classes that were created before 7.1 will have a definition as well.
Class structure

ECLASS consists of a four-level hierarchy of classification classes (i.e. a tree structure), the first level being the most general, the fourth level being the most specific. For the relation between levels there is a free inheritance relation. This allows the construction of a hierarchy of technical, commercial or other considerations, regardless of "mathematical" dependencies. It is important that at the lowest level (sub-group) classification of all classes are listed, which are required as part of the application. From top to bottom these hierarchical levels are:
The hierarchy of the classification classes is represented with the help of the coded name, i.e. the class code. The coded name consists of an 8-digit integer number, two digits for each hierarchical level. The number of trailing zeros in the end indicates the level of hierarchy, e.g. 16-00-00-00 (Segment "Food, beverage, tobacco"), 16-04-00-00 (Main group "Fruit"), 16-04-03-00 (Group "Berry fruit"), 16-04-03-01 (Commodity class "Blackberry"). The fourth level, the commodity class or product group is then further described with the help of properties and property values. Properties and values form the basis for the product description. See also figures 1 and 2 for an example:
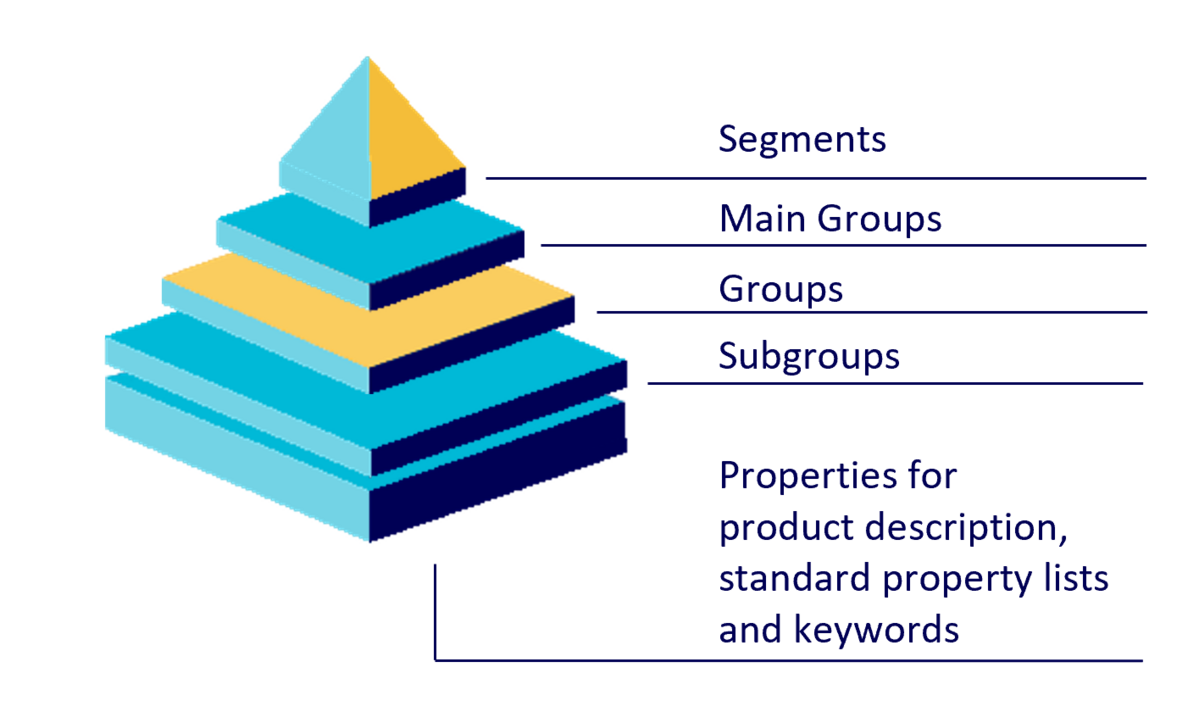
Figure 1: The ECLASS tree structure
Segment
A segment is the most general categorization and usually represents a certain branch or market. The current release 10.1 comprises 38 segments and an additional interim class (90-90-90-90). Figure 3 lists the ECLASS segments with the number of included classes and properties and, if available, their definition.
The ECLASS segments (release 11.0)
| Segment Number | Segment Name | Segment Definition | No. of classes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Development (Service) | Scope of segment 13 are all services of logistics. The segment 13 is divided into the following main groups: Concept development, Mechanical construction, Function development, Design/styling, Calculation/simulation, Product tryout, Production development, development care, Motor vehicle development, and Component development. The research and ideas that flow into development processes, such as Feasibility analysis', Patent and licensing, Product surveying, and Product optimization belong to the main group Concept development. | 305 |
| 14 | Logistics (Service) | Scope of segment 14 are all services of logistics. The segment 14 is divided into the following main groups: load securing, transport service, cleaning of transport mean, unload service, load service, transship service, and warehousing service. Special and combined logistics services belong to the main group value-added service (logistics) | 495 |
| 15 | Maintenance(Service) | Scope of segment 15 are all services of maintenance. Structure: The segment 15 refers to the German National Standard (Grundlagen der Instandhaltung). According to this Standard the maintenance types are being | 1.189 |
| 16 | Food, beverage, tobacco | The segment includes nutrition products of all varieties (e.g.'bread, bakery products and pasta', 'Seafood', 'Dairy product & egg','meat, poultry (minimally processed)', 'meat, poultry (raw, minimally processed)', 'beverages' and many more on the main group level). Besides regular nutrition products it also contains the segment 'Tobacco, smoking product and substitute' as a main group. | 336 |
| 17 | Machine, device (for special applications) | In segment 17, special purpose manufacturing or processing machines for a variety of industries are standardised. The main groups of this segment are divided by industries including: food processing, textile, clothing & leather, paper, construction, plastic & rubber, wood working, agriculture, graphic & arts, automated elctric trade and more. | 573 |
| 18 | Equipment f. mining, metallurgical plant, rolling mill a. foundry | This segment, typically features product classification of heavy industry equipment such as mining, metallurgical, rolling mills and foundry. The segment includes 18 main groups that divide equipment types, mostly by the material that has to be processed and/or how it is processed, for instance: metal, steel casting, melting NF metal, production of rolled profiles, production of tubes, forging, extruding and more. | 370 |
| 19 | Information, communication and media technology | This segment does not only contain telecommunication devices, antenna technology and multimedia-, entertainment-technology and much more for home, office and industrial use; it also contains software (e.g for server opration, cell-phone operation, video gaming and more), display technology, radio, mass storage and filming and camera equipment. The segment is very far developed with main groups ranging across 28 different groups of products. | 1.222 |
| 20 | Packing material | Besides familiar packaging types such as bags, cans, buckets, bottles, canisters, capsules, canisters, cartridges, boxes and crates (all called 'packing material'), this segment also includes 'package insert'-materials, 'packaging aid' (e.g. carton sealing tape) and 'food sales packaging' among other main groups. | 873 |
| 21 | Manufacturing facility, workshop equipment, tool | The segment primarily features rather lighter workshop equipment and tools. However, the scope of the segment is slightly larger than just these main groups as it also includes the main groups: facility, standardized tool parts, transport device, surveying equipment as well as cleaning devices and more. | 3.250 |
| 22 | Construction technology | Segment 22 is fairly broad in scope and far developed, as it features 47 main groups that really cater to the specificities of the various construction-skills, -tools, -service and -products required. Consequently the structure of the main groups is rather loose in its division by either type of work, type of product, product requirement, material, or work requirements. Main groups most notably even include: construction chemicals, construction service skill category; dewatering, drainage & shaft; roofing supplement unit, roof lighting; barrier, security device (construction), system for solar energy usage and more. | 2.126 |
| 23 | Machine element, fixing, mounting | The product description in segment 23 is aimed specifically at very detailed parts of various industrial machines. This can include seals, dampers, springs, screws, fastening aids; part-fitting, -hinge or -closing; gear units, breaks, wheels, pipelines, rotors and many more. | 1.945 |
| 24 | Office product, facility and technic, papeterie | Consumer and investment products in commercial office and in private use, including school supplies. The areas are described as office supplies | 1.869 |
| 25 | General service | included are all services, which are not part of one of the specialized service-segments like maintenance or logistics | 1.483 |
| 26 | Energy, extraction product, secondary raw material and residue | this segment comprises in a broader sense energy and raw materials as well as secondary substances. Typical of the products is a non-uniform chemical composition, which is either predetermined by the natural occurrence or the technical production processes. These include crude oil and raw gas with approximately the first processing stages, mining, mining and quarrying products, but also raw materials from renewable resources and non-processed biomass. In contrast to the SG 39 as methyl esters of palm oil fatty acids, which are derived directly from natural fatty acids of palm oil, are listed in SG 26, while a Palmitinfettsäuremethylester is an ester of a chemically defined acid and is therefore covered by SG 39. Energy and energy sources and supply (heat, cold, different qualities of water for industrial processes, industrial gases) are also listed in SG 30 | 296 |
| 27 | Electric engineering, automation, process control engineering | This segement includes devices that use, supply or transform electric energy in a variety of ways. It ranges from generators, transformers, switchgears, cables/wires and batteries to a variety of lightning devices, signals, controls, sensory technology, robotics and many more applications. | 3.583 |
| 28 | Automotive technology | This segment covers automotive technology in a very broad scope (meaning that it does not just include automobiles), which ranges from lifting vehicles (e.g. cranes), railbourne vehicles, trailers, containers and farming vehicles, to bicycles, aircraft, spacecraft and special vehicles. | 406 |
| 29 | Home economics, Home technology | The segment contains 18 main groups that are primarily ragarding household products including: kitchen-modules or -equipment, household appliance, dishes, cleaning, dispensers, household textiles, child- & baby-care products, home technology and more. | 502 |
| 30 | Auxiliary supply, additive, cleaning agent | the structuring in of SG 30 is along the application area. This shall enable the user to describe and classify substances (products) for both chemical aspects as well as their application. Typically the chemical purity associated with the use intended effect is in focus. On the fourth level usually products are listed with the same scope, while in the segments 31, 38, 39, the fourth level corresponds to a chemical substance. The substances are often mixtures with the same application, sometimes with similar chemical or in some cases even a uniform structure. To exclude a dual classification with a polymeric chemical in such cases the use of a characteristic term in brackets after the fuel name is used. For mixtures or polymers that are not clearly characterizable no unique CAS number is assigned | 1.459 |
| 31 | Polymer | Scope: All chemical compounds, which consist of a multiplicity of monomeric units, as far as they are of technical importance, pure, at room temperature stable and can be clearly characterised by a Chemical Abstracts Number. Specialties: The polymeric compounds are overwhelmingly of organic nature. Oligomeric compounds belong to Segments 38 and 39. Polymers, which differ only in the number of their monomeric units, have the same eclass Number, e.g. PE and LLDPE. Structure: Segment 31 is structured according to a) the elements which form the main chain such as Carbon, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulfur and Silicon, b) the character of the substituents in the side chain, c) the number of C Atoms per monomeric unit | 974 |
| 32 | Laboratory material, Laboratory technology | Consumables and instruments used for the execution of experiments. Typically used in research and quality control in chemistry, physic, biology, pharmaceutic medicine and partial engineering. Place of usage is often a laboratory, but it can be a another place outside or inside too | 895 |
| 33 | Installation (complete) | A segment that is primarily concerned with the standardization of production-plants & facilities ranging across the following industries: chemical & pharmaceutic, infrastructure, metallurgical, food processing, surface technology, agriculture, heating & refrigeration and many more. It consists of 21 mostly industry- or technology-themed main groups. | 730 |
| 34 | Medicine, medical technology | SG34 deals with products that are applied in health care, precaution and aftercare. The medical field is reserved to pharmaceutical and medical products. The highest regulatory authority is the BfArM (Bundesinst. f. Arzneimittel u. Medizinprodukte). Pharmaceutics is a science that deals with the consistence, impact, development, examination, production and delivery of medical products into the industry and pharmacies. It combines various aspects from other natural sciences, especially chemistry and biology. Medical technology combines knowledge from technical fields, especially problem solving and development, with the know-how of doctors, caretakers and other professions to improve diagnostics, therapy, nursing, rehabilitation and quality of life of people. The field of medical technology is divided into commodity products that are used for patient care taking on one hand and equipment and complex solutions that are used for patient monitoring and analysis of special questions on the other hand | 3.355 |
| 35 | Semifinished product, material | Segment 35 describes industrial products that can be of metallic or nonmetallic origin and can already serve as a slab or stick etc. for the production of sheets, plates, profiles, wires, etc. Also forging or turning parts etc. are included. Similarly, also yarns, raw materials are, tanned skins or paper can be included. Out of scope are any raw materials or finished products, i.e. only products that have not yet gone fully through the production process are described. Nor are solids, granules, powders, liquids or gases or chemical intermediates included. Segment 35 can have overlaps with the following neighboring segments: SG20 comprises paper and packaging films, SG21 includes welding or soldering materials, SG22 includes typical construction building materials such as concrete, paint, wood, wood panels, or plumbing pipes. With SG27 overlaps are possible in the field of cables and wires, with SG37 in the field of pipes and tubes | 888 |
| 36 | Machine, apparatus | Installation (complete): The operable totality of all interacting machines, appliances and components including services and / or software to perform a specific task / function. Machine, device (unit operation): Machines are devices for generating or transmitting power assembled from different parts / machine parts, making useful work or convert one form of energy into another. Apparatuses are devices for processing all types of materials by physical, chemical or biological processes. The machinery will be preferably used in industrial plants and industries. Certain groups of machines and equipment are out of scope of this segment: machine tool, electric power machinery, machine tools from vehicles and construction equipment. Machine, device (industry specific): The machinery can be used only industry-specifically due to their characteristics | 2.114 |
| 37 | Industrial piping | Segment 37 comprises pipes, pipe fittings and valves for the construction of pipe systems for industrial applications. This implies the supply of gas, water or district heating. The segment is not to be understood as a melting pot for all tubular semi-finished products | 637 |
| 38 | Inorganic Chemical | Scope: All chemical elements and all inorganic compounds, as far as they are pure, stable at room temperature, of technical importance and can be clearly characterised by a Chemical Abstracts Number. Specialties: Not comprised are a) structural isomers of elements except ozone, graphite and carbon black, b) isotopes and isotopic compounds except Deuterium, Deuterium oxide und Deuteriumn trioxide, c) aquous solutions except aquous carbonic acid and aquous Ammonium hydroxide. Structure: Segment 38 is structured according to the Periodic Table, starting with Carbon and Oxygen, their compounds and the (Earth-)Alkali-Carbonates (incl. Ammonium) and ending with compounds of subgroup VII to VIII | 1.631 |
| 39 | Organic Chemical | Scope: All organic chemicals incl. the D-, L- und DL forms as well as the reaction products of these compounds with Ethylene oxide, as far as they are of technical importance, pure, stable at room temperature and can be clearly characterised by a Chemical Abstracts, e.g. tartaric acid and Butanol ethoxylated. Specialties: Compounds which exist in the equilibrium between two or more tautomeric forms, e.g. Keto Enol Tautomers, are comprised only once. Structure: Segment 39 is arranged according to a) the structure of a compound with respect to its chemical composition, degree of oxidation and structure, b) starting with Carbon and Hydrogen, passing the further Heteroatoms (O, N, Hal, S, Si, P) and ending with Heterocycles | 5.668 |
| 40 | Occupational safety, accident prevention | SG40 lists items that contribute to secure the health of people from the effects of work processes directly or indirectly. The segment also includes devices to prevent that machines will be damaged or destroyed. The segment includes personal protective equipment in the broadest sense, as well as items for first aid, information resources on hazards and portable security devices such as gas warning devices or leak detectors, mechanical equipment, passive mechanical and active chemical systems as well as objects for the first attack. Not included are permanently installed electronic security devices or monitoring equipment whose majority share are electrical or electronic components | 805 |
| 41 | Marketing | Merchandising products and products needed for exhibition | 564 |
| 42 | In-vitro diagnostic | In-vitro diagnostic includes each medical device that is used as a reagent, reagent product, calibrator, control material, kit, instrument, apparatus, equipment or system, separately or in combination with the others, intended by the manufacturer to be used for the in-vitro examination of samples derived from the human body, including blood and tissue donations, and that serves solely or principally for the purpose of providing information. The information provides knowledge on physiological or pathological conditions or congenital anomalies or serves for the testing on safety and compatibility with potential recipients, or for monitoring therapeutic measures | 1.266 |
| 43 | Optics | The segment is a simple representation of different assets of optical enhancement tools, divided into the following main groups: optical material (e.g. glass, glass ceramics, plastic etc.), optical component (e.g. lens, prism, mirror, filter etc.), optical assembly (e.g. lens types vs. prims types), mounted optic (e.g. optics divided by how they are mounted) and optical instrument (e.g. microscope, telescope, periscope etc.). | 144 |
| 44 | Motor Vehicle | Segment 44 is a specifically aimed at a product description that is solely aimed at the automobile (including busses and motor trucks), excluding substantially different automotives. Main groups include the engine and exterior parts as well as interior parts, ranging across some of these topics: interior, exterior, electrics & electronics, energy storage, electric motor, transmisssion, air conditioning, communication/multimedia, body, motor vehicle and more. | 589 |
| 45 | Human and veterinary drug, pesticide as well as active ingredient | An assortment of main groups ranging across: medicine, active substance for pharmaceutical, active substances for veterinary drugs, active substances for plant protection and active substances for cosmetics. | 746 |
| 46 | Clothing and textile | The segment comprises of main product groups such as outer clothing, underclothing, accessory, shoes, sports- & functional-wear, sewing accessory 6 haberdashery and home textile. For each of these main groups, there is just one group in which '(other)' subgroups of the respective main group category can be found. On the subgroups level '(other, unspecified)' subgroups, respective to the group and main group can be found, however the class is currently not filled with product description. | 22 |
| 47 | Body care and personal hygiene | In this segment, the same strucuture and state of content development as in segment 46 applies to the following main groups: body care & body cleansing, facial care & facial cleansing, makeup & accessory, hair care & styling, oral care & dental care, intimate care & intimate hygiene, shaving & hair removal, perfume & fragrance, sun care & sun protection, contraception & birth control, pregnancy & nursing period and baby care & baby hygiene. The class is not filled with product description at this point. | 289 |
| 48 | Sport, playing, leisure | In this segment, the same strucuture and state of content development as in segment 46 & segment 47 applies to the following main groups: camping & outdoor, fishing & hunting, ball sports, water sports & boat sports, winter sports; gymnastics, fitness & dancing; equestrian sports; hiking, alpine sport & climbing, fighting sport, athletics; precision sport, bowl sport & shooting sport; cycling and musical instrument. The class is not filled with product description at this point. | 40 |
| 49 | Public safety and military technology | In this segment different types of product main groups for security in the public sector are described. the main groups include: ammunition, weapon, weapon system, weapon accessories; public safety & order and personal safety & protection. Under the main group named 'public safety & order' for instance, within the group 'access control, identity check', different types of body and cargo scanners as well as metal detectors or handcuffs were fed into the structure. | 242 |
| 50 | Interior furnishing | The main group structure in segment 50 is divided by the room of the house (e.g. living room) the furnishing belongs to. On the group level, the type of furniture (e.g. cupboard) is stated and on the subgroup level it is specified (e.g. cupboard, lowboard, sideboard highboard. The segment comprises of nine main groups that are far developed going deeper into the structure. | 494 |
| 51 | Fluid power | Starting from ECLASS Release 11.0, the two former main groups 27-29 Pneumatics and 27-30 Hydraulics were merged into this segment. Therefore, main groups 51-01 to 51-09 are filled with with pneumatics content such as actuators, valves, compressed air preparation, vaccuum technology and pneumatic connection technology, while main groups 51-41 to 51-57 are filled with hydraulics content such as pumps, motors, transmissions, power units and hydraulic accumulators. | 914 |
| 90 | Interim class (unspecified) | The interim class is used for structural content that has to be stored in order to move it to another existing segment, for restructuring purposes and for development of new segments under a nwe expert group. Groups (3rd level) for objects that cannot be classified into other specified groups in the existing structure, but that are classified to their parent-class on the 2nd level. A xx-xx-90-00-class cannot have any other sub-groups besides the generic xx-xx-90-90-class (…(Other, unspecified)) to be generally valid within the parent class on the 2nd level. Subgroups (4th level) for objects that cannot be classified into other specified subgroups in the existing structure, but that are classified to their parent-class on the 3rd level. | 4 |
Main group and group
Main groups on the second level and groups on the third level further devide product classes into more specific sub-groups.
Sub-group (commodity class or product class)
Sub-groups on the fourth level represent a commodity or a product class, i.e. a group of similar products. They are further described with the help of product properties and property values. Each sub-group has a 1:1-relation to an Application Class that includes these properties.
Class code (coded name)
The 8-digit class code (in ECLASS called: CodedName) consists of two digits for each of the four hierarchical levels. It is an arbitrary number and indicates where in the classification tree a product class is to be found. In contrast to the usual arbitrariness of classification codes, the ECLASS classification system uses certain specific class codes that have a meaning. They are called descriptive codes and they all begin with 9x. In contrast to the "quick guide for ECLASS-change requests" only the following descriptive codes are still being used in the ECLASS classification system:
xx-xx-90-00 (other)
Each main group (classification class on the 2nd level, e.g. 21-01-00-00) consists of at least the 90-class on the 3rd level, e.g. 21-01-90-00. The 90-class is the collective group for products that, following extensive checks, cannot be classified into other existing groups.
NOTE: Starting with ECLASS release 8.0 xx-xx-90-00-classes will
- only contain one generic sub-group xx-xx-90-90 ("Other, unspecified", see below). I.e. no xx-xx-90-01-classes will be allowed any more. This is planned to be corrected in MajorRelease 9.0.
All xx-xx-90-00-classes are described by the following generic definition:
Definition (xx-xx-90-00-class)
Group (3rd level) for objects that cannot be classified into other specified groups in the existing structure, but that are classified to their parent-class on the 2nd level. A xx-xx-90-00-class cannot have any other sub-groups besides the generic xx-xx-90-90-class (…(Other, unspecified)) to be generally valid within the parent class on the 2nd level
xx-xx-xx-90 (unclassified)
Each group (classification class on the 3rd level, e.g. 21-01-01-00) consists of at least the 90-class on the 4th level, e.g. 21-01-01-90. The 90-class is the collective subgroup for products that, following extensive checks, cannot be classified into existing subgroups.
NOTE: Starting with ECLASS release 8.0 90-classes will
- be renamed to (unspecified) as they are classified, but not further specified with the help of keywords or properties. I.e. they will be named as the parent class on the 3rd level plus (unspecified), e.g. 21010100 Knurling tool; 21010190 Knurling tool (unspecified).
- only exist on the 4th level
- do no longer contain keywords
- only Properties are permitted that are part of the following aspects
- Information
- Identification
- Attached Information
- Commercial
- Environmental footprint
- REACH
- WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment)
All 90-classes are described by the following generic definition, note and remark:
Definition (xx-xx-xx-90-class)
Sub-group (4th level) for objects that cannot be classified into other specified sub-groups in the existing structure, but that are classified to their parent-class on the 3rd level
Note (xx-xx-xx-90-class)
A 90-class is not further specified with the help of properties (apart from the basic properties) nor keywords in order to be universally valid within its parent-class on the 3rd level.
Remark (xx-xx-xx-90-class)
Assignments of products and services on a 90-class could be an indication that a more specified class structure is necessary and should therefore be requested.
It is planned to create the 90-class on the 4th level automatically when creating a new classification class on the 3rd level (group).
xx-xx-xx-91 (parts)
91-classes describe objects with spare part characteristics, without which the basic function of the product is not guaranteed.
NOTE: Starting with ECLASS release 8.0 91-classes will
- only exist on the 4th level
- be named as the parent class on the 3rd level plus (parts), e.g. 21010100 Knurling tool; 21010191 Knurling tool (parts)
- do no longer contain properties that describe the product itself, but only to identify the spare part or its relation to the product that the part is used for. This is to avoid that a certain product can be described as a distinct product class and as a parts-class for another parent product
All 91-classes are described by the following generic definition and note:
Definition (xx-xx-xx-91-class)
Sub-group (4th level) for objects with spare part characteristics that maintain or restore the original condition of the objects classified under the parent-class on the 3rd level
Note (xx-xx-xx-91-class)
The determination of the appropriate (spare) part (e.g. notebook display) takes place with the help of the name of the complete object that is to be maintained (e.g. notebook).
xx-xx-xx-92 (accessories)
92-classes describe objects with "add-on" characteristics, without which the basic function of the product is still guaranteed.
NOTE: Starting with ECLASS release 8.0 92-classes will
- only exist on the 4th level
- be named as the parent class on the 3rd level plus (accessories), e.g. 21010100 Knurling tool; 21010192 Knurling tool (accessories)
All 92-classes are described by the following generic definition:
Definition (xx-xx-xx-92-class)
Sub-group (4th level) for objects with complemental characteristics, without which the basic function of the objects classified under the parent-class on the 3rd level is still guaranteed
Blocked Class Codes
ECLASS has blocked the class codes 98 and 99 on all levels for company-specific use (see also: the blocked segments 98-00-00-00 and 99-00-00-00), i.e. ECLASS will not use these class codes on any level. A company may use them for internal purposes where needed.
- NOTE: We advice to not exhange these data with business partners as they might have used the same codes for their internal purposes and assigned them to different product groups.
- EXAMPLE: In segment 20 Packing material, a company might need to assign class codes to company-specific products that cannot be classified in ECLASS. A new ECLASS-class is not requested either as it is not needed. A company may now use a new main group 20-98-00-00 to create the new structure 20-98-01-01 for their own purposes, as well as 20-03-98-01 or 20-03-01-98. This way, a new struture on all hierarchical levels is possible in any existing segment.
Comparison
| Descriptive Code | Hierarchy | PreferredName | Properties | Keywords allowed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90-classes | Only on 4th level (exception for 90-90) | Preferred Name of the 3rd level plus (unspecified) | No properties allowed apart from basic properties | No |
| 91-classes | Only on 4th level | Preferred Name of the 3rd level plus (parts) | Properties restricted (i.e. BAF281) | Yes |
| 92-classes | Only on 4th level | Preferred Name of the 3rd level plus (accessories) | Properties allowed | Yes |
| 98-classes | All levels (1-4) | Company-specific | No restrictions | No restrictions |
| 99-classes | All levels (1-4) | Company-specific | No restrictions | No restrictions |
Element structure (Classification Class)
The following part will describe how the structural element "classification class" is structured and what attributes it consists of. All attributes are named in CamelCase writing. Attributes can be mandatory or optional, can be created automatically or manually be the user and underly certain rules. All of them are limited to a certain amount of characters.
Identifier (Classification Class)
The official and internationally unique ECLASS identifier, i.e. primary key, is the IRDI (International Registration Data Identifier), a globally unambiguous identifier that comprises Supplier+TypeOfSE+Identifier+VersionNumber. The separate export of Supplier, ID, VersionNumber and the Identifier (ID+ VersionNumber) is therefore redundant. Starting with ECLASS Release 8.0 this redundant information will no longer be additionally exported, because it is already contained in the IRDI which is the only valid primary key in ECLASS.
The identifier for classification classes is the IrdiCC. It is mandatory, automatically created and limited to 20 characters. TheTypeOfSE of a class is 01.
Coded Name
See Class code (coded name), the attribute is called CodedName and is a mandatory field.
Preferred Name (Classification Class)
The text attribute named PreferredName is the official name of the product class and is a mandatory text field. The following rules apply to the PreferredName:
- 80 character limit
- is a unique name, i.e. does not exist more than once in the ECLASS classification system
- Begins with a capital Letter in any language where capital letters exist
- no special characters allowed
- Must not contain a trademark, company or brand name
- It should be possible to use the preferred name within a continuous text , i.e.
- Adjective before noun (German, English)
- Lower case for adjectives
- Avoid combinations of several terms, keywords/synonyms are denoted separately
- Give preference where possible to the basic grammatical form (singular, infinitive)
- The following special characters must be avoided: semicolons (;), inverted commas (")
- Do not use additions which resemble properties
Definition (Classification Class)
Today, the class definition is a mandatory text field. The objectives and rules are described below.
Objectives of class definitions
- Objective 1: a class definition shall describe the product class and give more information in order to make it easier for
- Quality check
- Users to find their product group
- Translators to find the right terminology
- Users of other standards to map/match/harmonize
- Objective 2: The quality check of definitions shall be content-oriented, less form-oriented.
- Objective 3: From 1st to 4th level the definition shall go from general to specific.
- Objective 4: The definition shall deliver details what kind of products are to be found in the class.
- Objective 5: Every class (all levels) in ECLASS shall have a definition with release 8.0 latest.
Rules for class definitions
- 1023 character limit
- no special characters allowed
- formal rules must be considered:
- start without a definite or indefinite article
- start with a lower case letter (unless it is a German noun)
- do not end with a full stop or any mark
- A definition shall deliver information on
- how and why the class is distinguished from its neighboring classes (i.e. distinction criteria of neighborhood)
- how and why the class is distinguished from other related classes (i.e. distinction criteria of similar classes in other segments).
- A segment’s definition shall describe the segment and what is generally included (branch, market etc.).
- A definition of a segment, main group and group shall describe the classification criteria of their sub-groups, i.e. describe how the sub-groups, i.e. subordinate class levels are distinguished from each other (e.g. by material, application, area, etc.).
- Descriptive codes have a generic (maybe automatically created) definition (and note, remark where available), see above.
ISO Language Code
see ISOLanguageCode
ISO Country Code
see ISOCountryCode
Note (Classification Class)
Note on definition, optional, created by user, limited to 1023 characters.
Remark (Classification Class)
Remark on usage of the class, optional, created by user, limited to 1023 characters.
Release notes (Classification Class)
The description of a classification class in the BASIC release notes is as follows (update: Release 7.1):
Class table
| No. | Attribute Name | Description | Length |
| 1 | Supplier** | International Code Designator (0173-1 for ECLASS) | CHAR(6) |
| 2 | IdCC** | Identifier + VersionNumber | CHAR(9) |
| 3 | Identifier** | Identifier (unique within the structure element type: class) | CHAR(6) |
| 4 | VersionNumber** | Version number | CHAR(3) |
| 5 | VersionDate | Publication date of version | CHAR(10) |
| 6 | RevisionNumber | Revision number | CHAR(2) |
| 7 | CodedName | ECLASS coded name | CHAR(8) |
| 8 | PreferredName | Name | CHAR(80) |
| 9 | Definition | Definition | CHAR(1023) |
| 10 | ISOLanguageCode | Language code according to ISO 639-1 / ISO 639-2, e.g. "en" | CHAR(2) |
| 11 | ISOCountryCode | Country code according to ISO 3166-1 / ISO 3166-2, e.g. "US" | CHAR(2) |
| 12 | Note | Note on definition | CHAR(1023) |
| 13 | Remark | Remark on usage of the class | CHAR(1023) |
| 14 | Level | Hierarchical level in class tree | CHAR(1) |
| 15 | MKSubclass | Flag subgroup (0=no / 1=yes) | CHAR(1) |
| 16 | MKKeyword | Flag, if keywords exist for class (0=no / 1=yes) | CHAR(1) |
| 17 | MKBSA | Flag standard set of properties (2=Standard set of properties (SSP))* | CHAR(1) |
| 18 | IrdiCC | Primary key of the class; International Registration Data Identifier of the class, globally unique ECLASS Identifier (Supplier+TypeOfSE+Identifier+VersionNumber) | CHAR(20) |
* ECLASS differentiates between standard and basic sets of properties (SSP, BSP). SSP are individually developed for specific classes. BSP (one for each segment) since ECLASS 6.1 basically consist of at least the following properties:
BAA271004 "GTIN" (before 6.1: "EAN code")
BAA001003 "Manufacturer name"
BAA059004 "Supplier product number"
BAD847003 "Manufacturer product number"
BAA316003 "Product name"
BAA002002 "Product type description"
BAB542001 "Supplier name"
The entries in the field "MKBSA" have the following meaning:
No entry = Basic set of properties (BSA)
2 = Standard set of properties (SSA)
Change Request
How to request a change on a classification class in the ECLASS ContentDevelopmentPortal?
Please see here: Classification Class (Create Change Request)
Rules for the creation of a change request are described here: General rules for Change Requests