3.2 Fixing Variants
Chapter navigation
General
In this block area, fixing variants, information on the fixing of the article is given.
Via the property Number of fixing variants you call up the block fixing variant according to the number of possible fixing variants (e.g. quick and screw fixing).
Level | Type | Structure element name | Application, explanation | Function for CAx and process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | C | number of fixing variants | Selects the block for the description of the fixing variants according to number | |
1/2 | B | Fixing variant | Block fixing variant | Block for description of fixing variants |
3 | M | name of fixing variant | Name of the fixing variant. For standard fixings with top-hat rails we recommend: TH15, TH35, TH75. For systemic fixing, please select alphanumeric names without spaces. | Helps with the allocation and arrangement of components |
3 | M | type of mounting | Information on the type of mounting | Relevant values/oil |
4 | W | flanged | Systemic screw or clamp mounting for flange parts | |
4 | W | clamped | Quick fixing on mounting rail | |
4 | W | pluggable | Mounting by plugging in, snap-in | Only use pluggable and not the value pluggable (adapt for 11.0) |
4 | W | integrable | Systemic internal mounting | |
4 | W | Screw mounting | Fastening by screwing, turning, without or with screws or threaded bolts | |
4 | W | Bus bar fastening | Systematic fixing on busbars by clamping or screwing. | |
4 | W | Top-hat rail TH15 | Quick fixing on top-hat rail, width 15mm. | |
4 | W | Top-hat rail TH35 | Quick fixing on top-hat rail, width 35mm. | |
4 | W | top-hat/g-Rail TH35/G32 | Quick fixing on top-hat/g-rail, width 35mm. | |
4 | W | G track G32 | Quick fixing on G-rail, width 32mm. | |
4 | W | Top-hat rail TH75 | Quick fixing on top-hat rail, width 75mm. | |
4 | W | 19 inch | Fixing on 19 inch carriers. | |
4 | W | Wall mounting | Screw fixing on the wall. | |
4 | W | Base attachment | Base fixing on the floor. | |
4 | W | direct-mounted | Article is mounted directly to another component using system parts. | |
4 | W | Slide-in module | Article is inserted system-specifically into an extension unit. | |
4 | W | insertion | Article is placed in a system-specific socket. | |
4 | W | welded | Fixation by welding process. | |
3 | M | Fixing supply point | Specifies the coordinate of the fixing supply point and its position. The fixing coordinates refer to this supply point. The fixing point itself refers to the article shape-dependent reference point (RP) see: 3.2 Fixing Variants#Usage of Fixing Point, Fixing supply point (in mm) | |
3 | M | fixing on another component possible | Indicates whether the article can be fixed upon another component. | Yes/No. Helps in positioning the article |
3 | M | fixing under another component possible | Indicates whether the article can be fixed under another component. | Yes/No. Helps in positioning the article |
3 | C | Number of mounting points | Mounting points are only necessary where the articles are fixed in a point-shaped manner, e.g. by screws. They are located on the fixing level (e.g. fixing plate, wall). | Selects the block for mounting point description - see |
3 | C | number of mounting cut-outs | If mounting cut-outs in panels and or fronts (touch protection covers, doors) are required, information on the required measurements can be given here. | Calls the block to describe mounting cut-outs - See |
3 | C | number of mounting orientations | Only if other mounting orientations are required, dependent on the fixing, than those already defined at item level under Mounting orientations. | Selects the block for the mounting orientation description - see |
3 | C | number of barred areas | Only if, depending on the fixing, other barred areas are required than those already defined at item level under barred areas. | Selects the block for description of barred areas - see |
3 | C | Number of parts relations | Only if, dependent on fixing, parts are required | Selects the block for the parts relations description - see |
Below is an example of a device, such as a contactor, that provides both a bus bar fastening (green) and a screw mounting (red).
red screw mounting
green for quick mounting

Figure 18: CAx-Basis example of screw and quick mounting variants
Example: Bus bar fastening
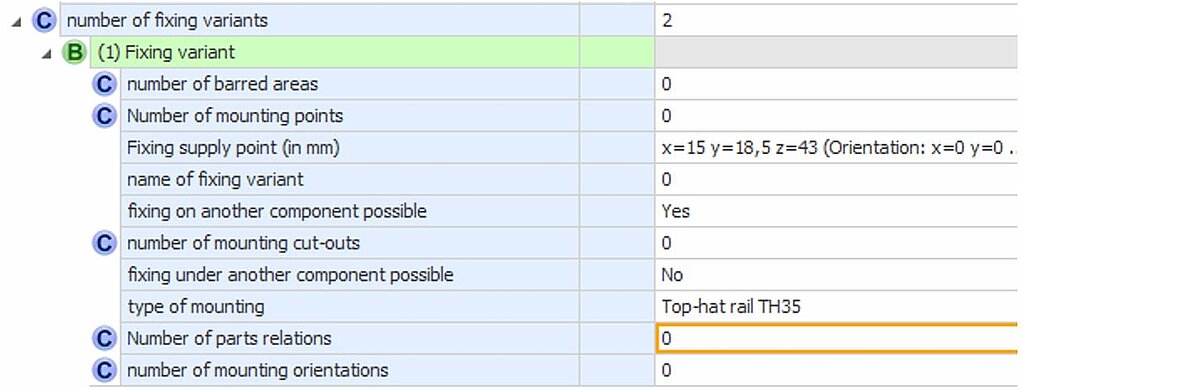
Figure 19: CAx-Basis example of fixing variant 1. Variant describes a quick mounting for a DIN rail
Example: Screw mounting
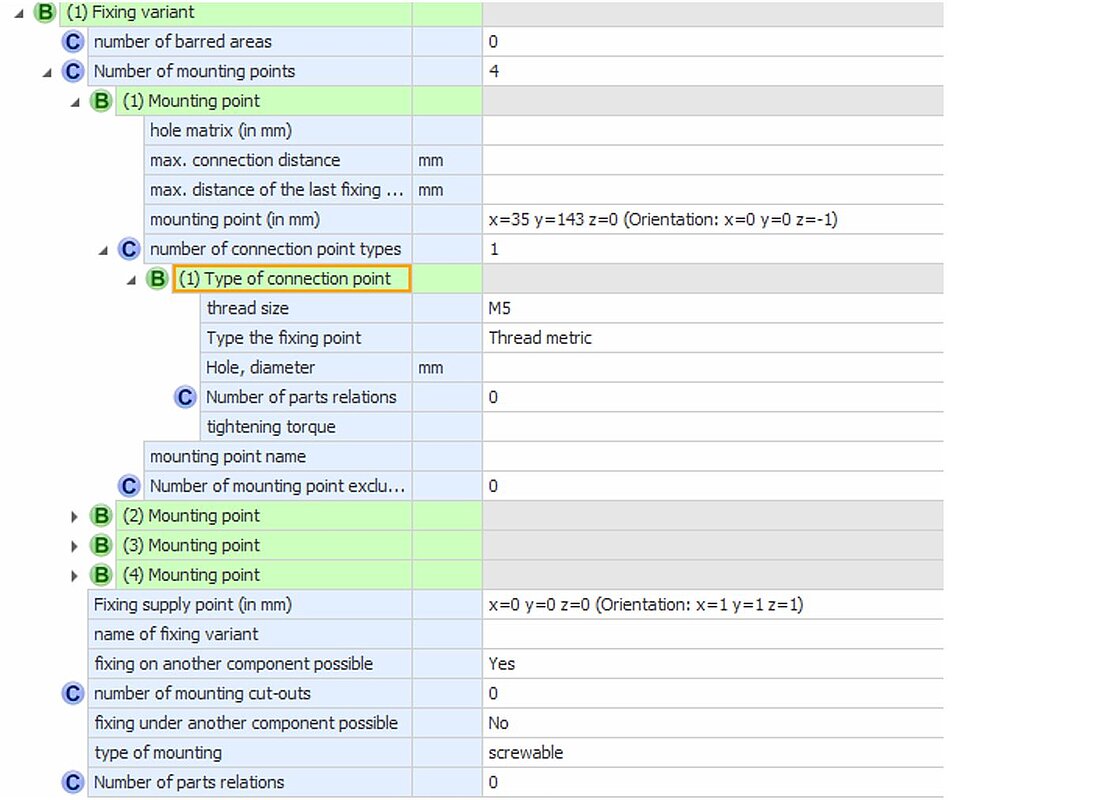
Figure 20: CAx-Basis Example of fixing variant 2. Variant describes a screw mounting for the same article
Mounting Point
The mounting points describe the information needed to perform the appropriate work for an assembly.
Level | Type | Structure element name | Application, explanation | Function for CAx and process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | B | Mounting point | Block mounting point | Block for mounting point description |
2 | M | mounting point name | Possibility of naming / marking the mounting point | Information assignment and protocol options |
2 | M | mounting point (in mm) | Indication of the coordinate of the mounting point and its positioning.
| Specification of a dot-shaped mounting point, e.g. screw, rivet... Is required in drilling automation to approach the point. For long material, the center of the first hole should be indicated in the direction of the line up. The Z axis represents the point of contact between the mounting surface and the product (usually Z = 0). |
2 | M | Hole matrix (in mm) | Here you can enter data in mm for a linear fixing matrix. (e.g. for long materials: bus bar, wiring duct) | Specification automatically helps the CAE system to set fixing points depending on the material. |
2 | M | max. connection distance | max. connection distance in mm between two required fixings for long material. | Specification helps the CAE system to automatically take fixing distances into account, depending on the material. |
2 | M | max. distance of the last fixing point to the end edge | Max. fixing distance of the last possible fixing point relative to the end edge of the long material. | This helps the CAE system to automatically set the last possible fixing point depending on the material. |
2 | C | number of connection point types | Indication of the number of possible connection point variants | Calls the block to the connection point type description according to number |
2/3 | B | 'Type of connection point | Block Type of connection point | Block for description of connection point type |
4 | M | Type of connection point | Block Type of connection point describes the design of the connection point | Block for description of mounting point type |
5 | W | Hole |
|
|
5 | W | Thread metric |
|
|
5 | W | thread inch |
|
|
4 | M | Hole diameter | Describes the hole diameter of the fixing point.
| Required for drilling automation to accomplish the drill hole size To be filled only if type of mounting point provides for "hole" |
4 | M | thread size | Describes the thread size of the fixing point (value list) | Required for drilling automation to complete the thread To be filled only if type of connection point provides for "thread xxx" |
4 | M | tightening torque | Manufacturer's specification for the required tightening torque of the fixing | Needed for assembly-screwdriver-automation |
4 | C | Number of parts relations | Only if other parts are required - depending on the fixing type - than those already defined at item level as parts relations. | Selects the block for the parts relations description - see |
2 | C | Number of mounting point exclusions | Indication of the number of possible mounting point-exclusions | Calls the block to the mounting-exclusion description according to number |
2/3 | B | mounting point exclusion | mounting point exclusion | Block for mounting point exclusion description |
4 | M | Exclusion Mounting name | Specification of the mounting point name to be excluded for the fixing in this variation. | To ensure that this point is not set as a mounting point in the CAE system. |
Usage of Fixing Point, Fixing supply point (in mm):
The component receptacle of a product and the fixing supply point of a product fixed on it are overlaid during assembly planning.
The order of the fixing points is not determined. If there are several options for usable fixing points, the standard fixing should be specified as the first variant.
Type of mounting=carrier rail
For products that are fixed on a carrier rail, the fixing supply point is in the middle and upper edge of the carrier rail in the direction of alignment at x=0 on the device.
When fixing on carrier rail, usually no fixing point is required. The fixing reference is described by the fixing supply point.
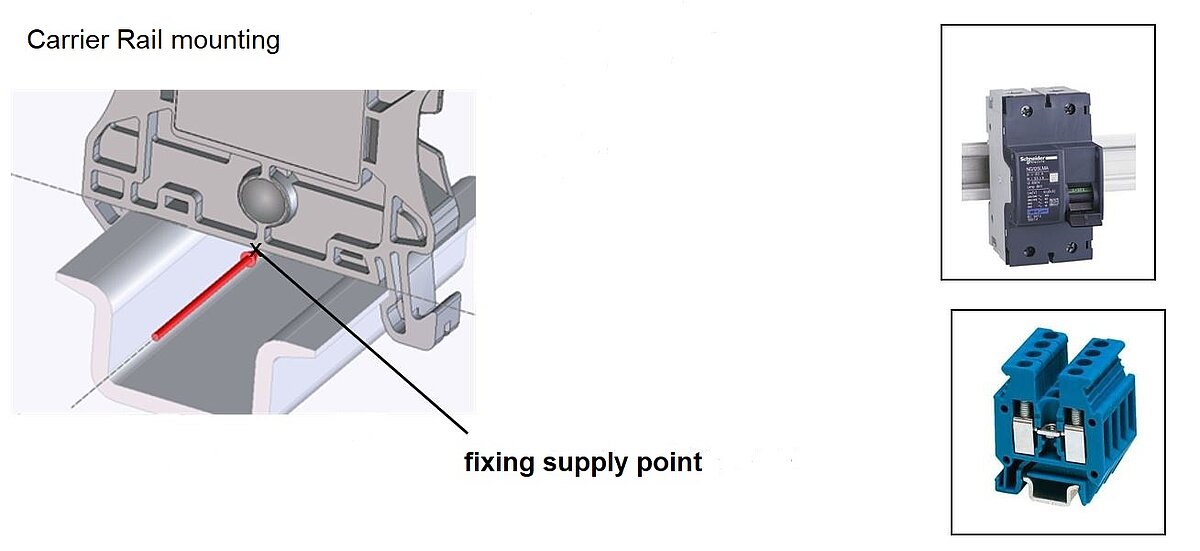
Figure 21: CAx-Carrier Rail mounting
Type of mounting=direct mounting
Corresponding also for screw mounting, wall mounting, ...
The fixing supply point should be selected so that it can be easily positioned for line-up and dimensioning.
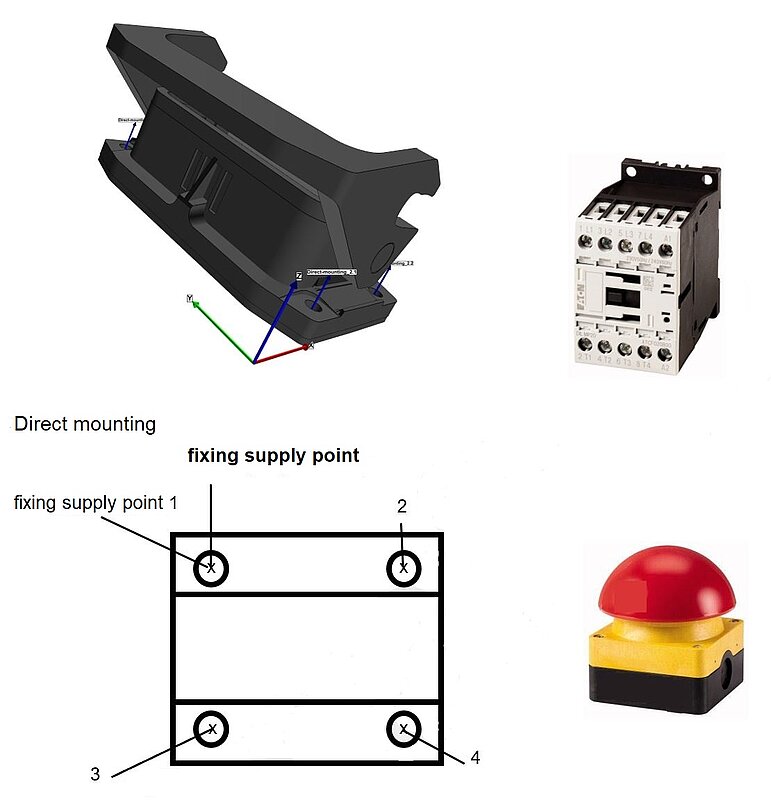
Figure 22: CAx-direct mounting
Type of mounting=bus bar fastening
The fixing supply point should be located on the top front edge of the top rail.

Figure 23: CAx-bus bar fastening
Type of mounting=front-mounting
Each type of mounting is to be defined here!!!
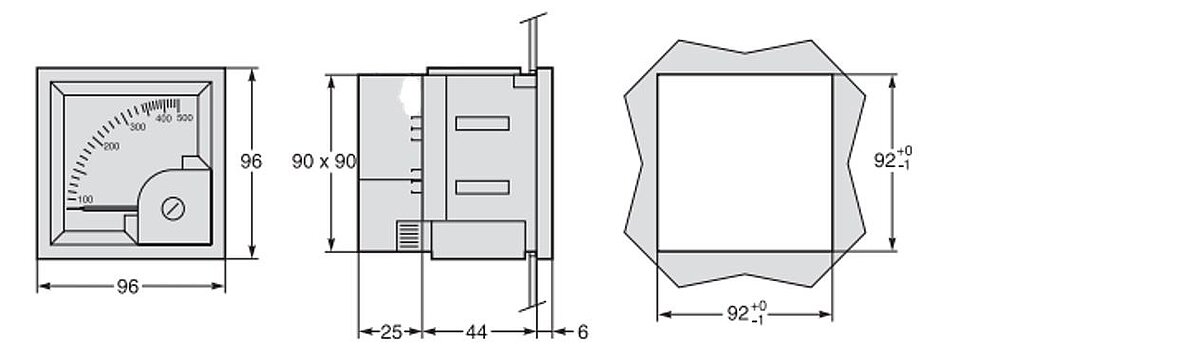
Figure 24: CAx-front-mounting
Mounting cut-outs
The properties can be used to describe a mounting cut-out for a piece of equipment. E.g. cut-out in the front for a measuring instrument or in housing walls for filter fans or for heavy connectors.
If mounting cut-outs in panels and or fronts (touch protection covers, doors) are required, information on the required measurements can be given here.
All positions are given as Axis-1D properties. Only the positioning values are relevant, the direction values are irrelevant. The X- and Y-values are decisive for the size of the cut-out, the Z-axis is to be selected equal to the value of the Z-axis of the fixing supply point for the cut-out in the panel/front.
Level | Type | Structure element name | Application, explanation | Function for CAx and process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | C | Number of mounting cut-outs | Select block mounting cut-out. Application for front mounting devices and penetrations of covers | Selects the block for the mounting cut-out description according to number |
1 / 2 | B | Mounting cut-out | Block Mounting cut-out | The mounting cut-out is described by combining different profiles. E.g. in the door |
3 | C | Number of contours | Select Block contour | Selects the block for contour description according to number |
3 / 4 | P | Contour | Request contour shape polymorphic | Enables contour-dependent partial section descriptions |
5 | W | Line | Identification of the polymorphic block line | Selects the block for cut-out-line description |
6 | M | Starting point (in mm) | Coordinates of the starting point of the line. Indication in mm, reference to the supply point of the article. | Is required for the preparation of the cut-out by milling or pressing machine. |
6 | M | Final point (in mm) | Coordinate of the final point of the line | Required for cut-out creation |
5 | W | circular arc | Identification of the polymorphic block circular arc | Calls the block for circular arc cut-out description |
6 | M | Midpoint (in mm) | Coordinates of the midpoint of the circular arc. Indication in mm, reference to the supply point of the article | Selects the block to describe mounting cut-outs. |
6 | M | Radius | Radius of the circular arc in mm. |
|
6 | M | Starting angle | Starting point in degrees of the circular arc. | Zero degree is "right" on the x-axis. |
6 | M | End angle | End point in degrees of the circular arc.
| Zero degree is "right" on the x-axis. The cut-out starts at the starting angle and runs counterclockwise to the end angle (polar coordinate system). |
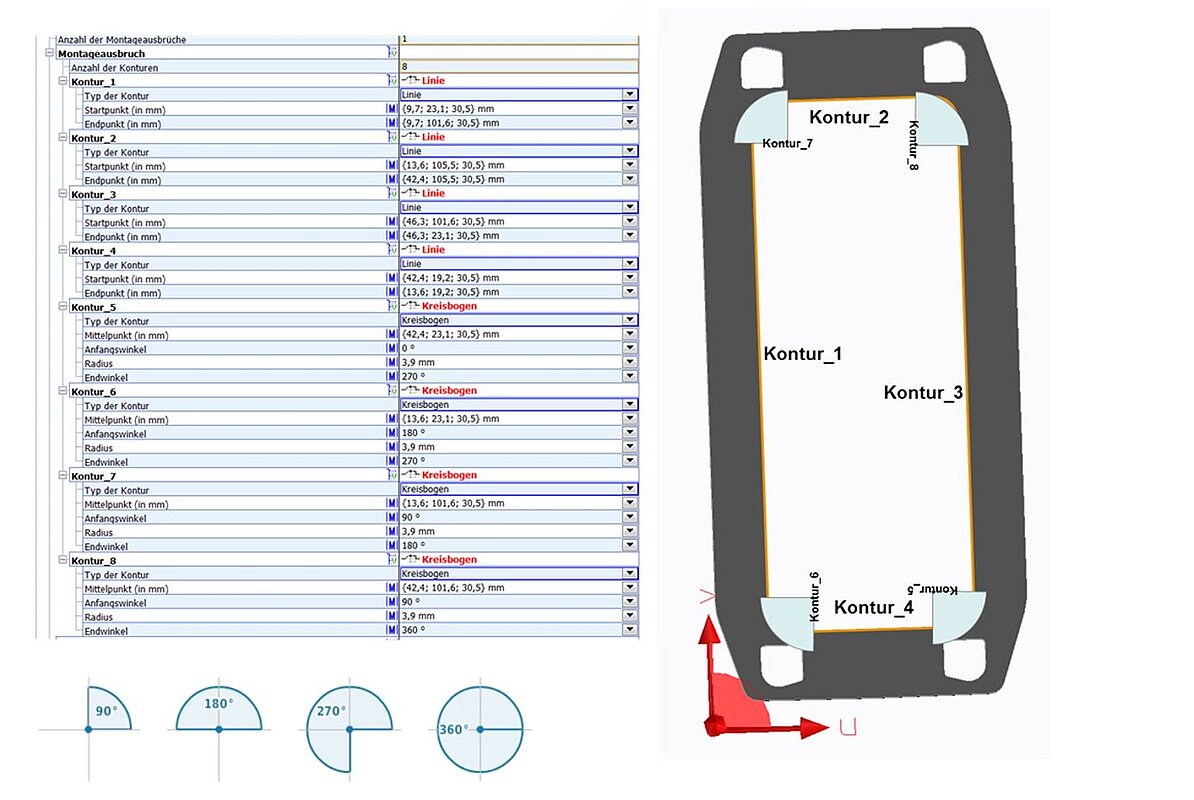
Figure 25: CAx-Basis mounting cut-out
Example: Ammeter
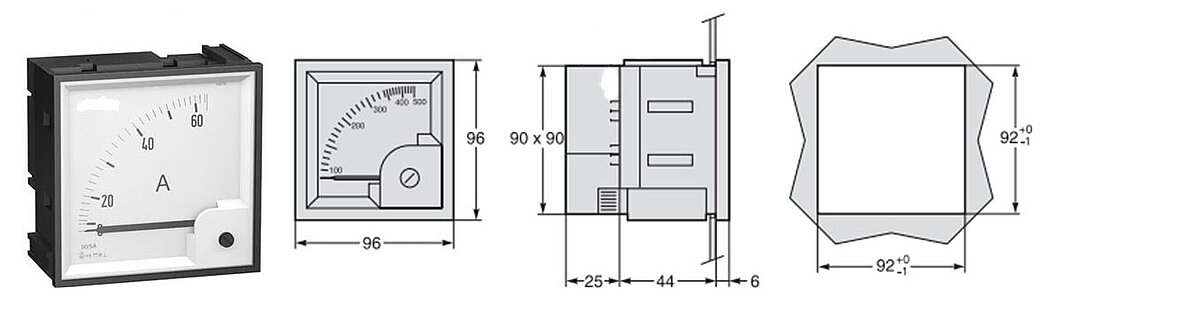
Figure 26: Ammeter illustration and 3 sides of the ammeter
Example: rectangular cut-out
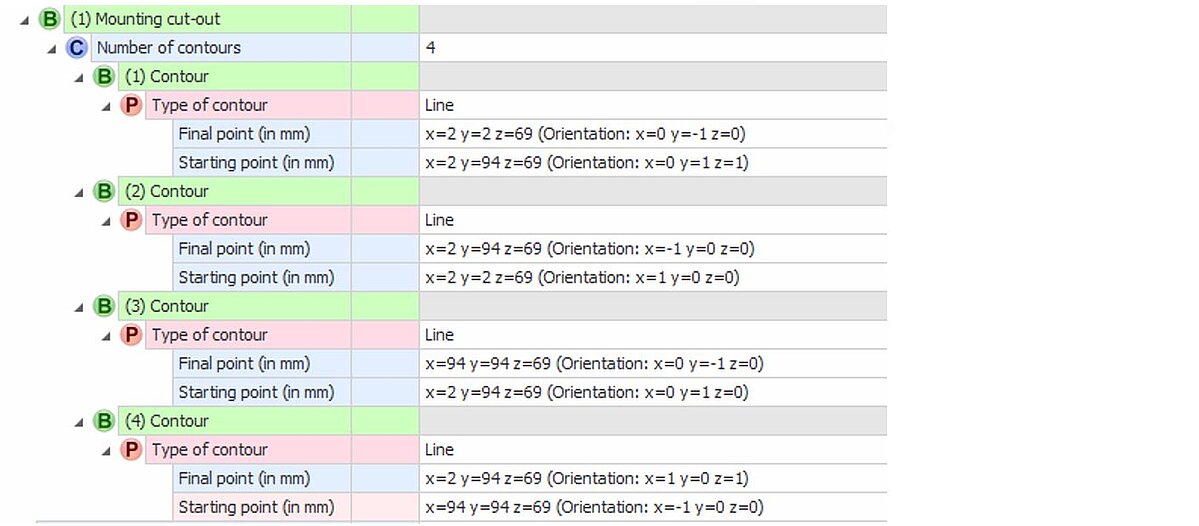
Figure 27: CAx-Basis example of measuring instruments front-mounting