Products
The ECLASS association publishes the following products related to the ECLASS Standard: The official ECLASS releases, Release Update Files (RUF), Transaction Update Files (TUF). Which one of these products is suitable for a company depends on the area of application and the company’s objectives. Since Release 7.0, the ECLASS standard is available in two different export formats. In the frame of internationalization adjustments according to ISO standards were needed. Significant adjustments involved both a distinction between ISO-standard conformant “closed” value lists and “open” proposal lists and the introduction of standard compliant measurement units.
The ECLASS Standard is being published in regular updates, the ECLASS Releases. The first ECLASS Release 3.0 was published in 2000 and contained about 15.000 classes, but no properties yet. With ECLASS 4.0 properties, values and keywords were published additionally to classification classes for the first time in 2003. With ECLASS 6.0 a data model according to ISO 13584 was created. ECLASS 7.0 was the first release that is available in a BASIC and an ADVANCED version. Some ECLASS Releases are published in various language versions. The current Release 12.0 is available as ECLASS 12.0 BASIC (CSV), ECLASS 12.0 BASIC (XML), ECLASS 12.0 ADVANCED (XML). New updates of the ECLASS Standard are published along the release process.
BASIC Version
The BASIC version contains all elements that were already available before Release 7.0: classification classes, keywords, properties, values, units, synonyms. 7.0 BASIC is available in a .csv-format and a .xml-format. The usual CSV export format of the ECLASS-standard includes eight CSV files, which Office programs such as MS-Excel® and MS-Access® can process and implement. The ReadMe pages describe the amendments, structure, contents, and relations of the CSV files. With effect from ECLASS 7.0, it will also be available as an additional export format in ECLASS XML format for automatic ECLASS standard processing. This export format bases on an ISO-standardised XML format for product data exchange. Related specifications are published in ISO 13584-32:2010 (ontoML). These specifications offer a uniform and comparable data structure for communications between machines. Consequently, two export formats are available for processing and implementing BASIC representation. Export of ADVANCED representation is only available in ECLASS XML format.
Update 2018-05-07: Due to a request of an ECLASS member, the ECLASS association decided to publish the Releases 5.1.4 and 6.0 subsequently also in XML format, for the languages German and English.
The BASIC version is mapped to the ADVANCED version. This Mapping table enables users of the ADVANCED to exchange technical data with users of the BASIC. Hereby, the necessary know-how has to be delivered by the user of the ADVANCED.
Release Sizes
| Release | Publication date | No. of classes | No. of properties | No. of values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 2000-04-30 | 4,785 | 2,427 | 1,986 |
| 4.0 | 2001-03-27 | 12,915 | 2,303 | 1,982 |
| 4.1 | 2002-02-28 | 15,315 | 5,504 | 3,143 |
| 5.0 | 2003-09-02 | 24,870 | 3,667 | 1,287 |
| 5.0.1 | 24,919 | 3,699 | 1,576 | |
| 5.1 | 2004-09-27 | 25,658 | 5,525 | 4,544 |
| 5.1.1 | 2005-09-07 | 27,216 | 6,941 | 4,546 |
| 5.1.2 | 2006-07-12 | 27,442 | 6,964 | 4,712 |
| 5.1.3 | 2006-10-26 | 30,280 | 6,967 | 4,712 |
| 5.1.4 | 2007-07-01 | 30,329 | 7,136 | 4,720 |
| 6.0 | 2008-04-30 | 32,592 | 8,653 | 6,811 |
| 6.1 | 2009-08-21 | 32,795 | 9,910 | 7,531 |
| 6.2 | 2009-12-01 | 32,832 | 9,919 | 7,533 |
| 7.0 BASIC | 2011-02-15 | 37,868 | 15,397 | 19,123 |
| 7.1 BASIC | 2011-11-30 | 39,068 | 15,953 | 19,874 |
| 8.0 BASIC | 2012-12-02 | 39,041 | 16,137 | 13,609 |
| 8.1 BASIC | 2013-12-02 | 39,083 | 16,202 | 13,804 |
| 9.0 BASIC | 2014-12-08 | 40,870 | 16,845 | 14,365 |
| 9.1 BASIC | 2015-11-30 | 41,027 | 16,973 | 14,456 |
| 10.0.1 BASIC | 2017-02-03 | 41,647 | 17,342 | 15,708 |
| 10.1 BASIC | 2018-03-29 | 42,220 | 18,867 | 17,022 |
| 11.0 BASIC | 2019-07-29 | 45,293 | 19,085 | 24,979 |
| 11.1 BASIC | 2020-08-10 | 46,135 | 19,329 | 25,779 |
| 12.0 BASIC | 2021-11-22 | 47,321 | 21,600 | 27,455 |
| 13.0 BASIC | 2022-12-14 | 47.933 | 21.730 | 27.717 |
| 14.0 BASIC | 2023-11-20 | 48.170 | 22.996 | 29.358 |
| 15.0 BASIC | 2024-11-29 | 48.301 | 22.770 | 30.667 |
| 16.0 BASIC | 2025-11-27 | 48.283 | 23.093 | 31.185 |
ADVANCED Version
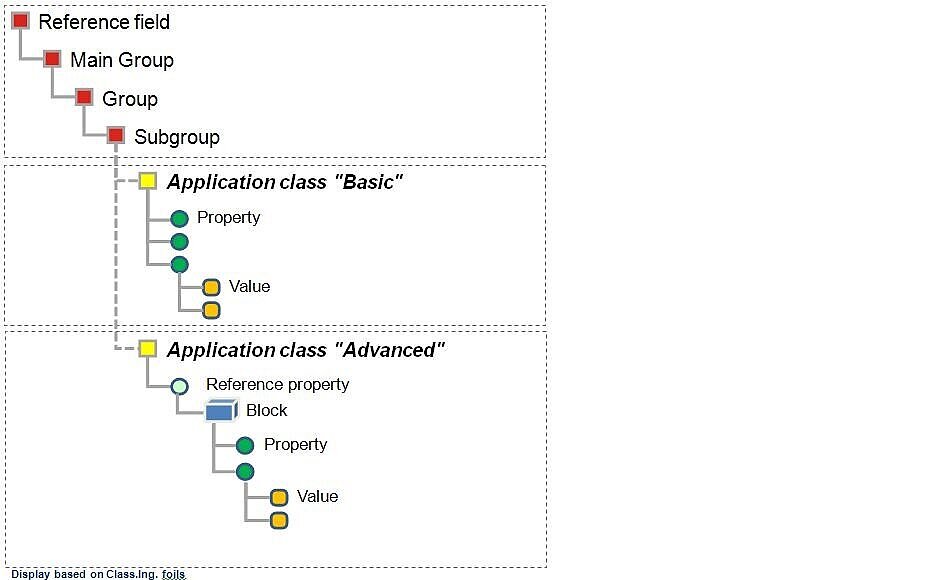
With effect from ECLASS 7.0, the ECLASS standard is available in an ADVANCED version that provides more possibilities for the user, but is therefore technically more complex. It contains dynamic elements such as dependant properties, polymorphism and cardinality and properties are structured in blocks. It is therefore only available in an XML format. By introducing ECLASS 7.0 ADVANCED representations, the ECLASS-Association offers the first ISO conformant data structure.
The BASIC version is mapped to the ADVANCED version.
The data structure contains the structural elements described under Structure and structural elements. The result is the following structural arrangement:
The 4-level class structure is associated with the new application class (AC). This, in turn, contains all relevant structural elements such as blocks and aspects. Integration of both the PROLIST standard and CAx elements results in additional important data model extensions. Using “Cardinality" multiplication elements as well as variant access of special blocks by means of “Polymorphism” results in significant simplification.
Implementation of additional data type extensions (Level-Type and Axis-Type) results in further simplifications. Consequently, a single data type combines physical-technical relations of different properties.
The complex data model has to be transfered in a data structure configured for that purpose. That is why ECLASS 7.0 uses ontoML rules defined in ISO 13584 – part 32. These rules describe the form and arrangement of the structural elements and predefine how to interpret the ontoML in order to be able to process ECLASS 7.0 ADVANCED Representation from a data-technical point of view.
Export Format
Starting with Release 7.0 the ECLASS standard is available in two different formats: .csv and .xml. The BASIC version is available in both .csv and .xml, the ADVANCED version is only available in .xml. Before Release 7.0 any ECLASS version was only available in .csv format.
Update 2018-05-07: Due to a request of an ECLASS member, the ECLASS association decided to publish the Releases 5.1.4 and 6.0 subsequently also in XML format, for the languages German and English.
In the frame of internationalisation adjustments according to ISO standards were needed. Significant adjustments involved both a distinction between ISO-standard conformant “closed” value lists and “open” proposal lists and the introduction of standard compliant measurement units.
Below you find a matrix which release is available in which export format:
| Product | File Format |
|---|---|
| ECLASS 16.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.2, ECLASS XML 5.0 |
| ECLASS 16.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 5.0 |
| ECLASS 16.0 ASSET | ECLASS XML 5.0 |
| ECLASS 15.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.1, ECLASS XML 5.0 |
| ECLASS 15.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 5.0 |
| ECLASS 15.0 ASSET | ECLASS XML 5.0 |
| ECLASS 14.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.2, ECLASS XML 4.0 |
| ECLASS 14.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 4.0 |
| ECLASS 14.0 ASSET | ECLASS XML 4.0 |
| ECLASS 13.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.1, ECLASS XML 3.1 |
| ECLASS 13.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 3.1 |
| ECLASS 13.0 ASSET | ECLASS XML 3.1 |
| ECLASS 12.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.0, ECLASS XML 3.0 |
| ECLASS 12.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 3.0 |
| ECLASS 11.1 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.0, ECLASS XML 3.0 |
| ECLASS 11.1 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 3.0 |
| ECLASS 11.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.0, ECLASS XML 3.0 |
| ECLASS 11.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 3.0 |
| ECLASS 10.1 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.0, ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 10.1 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 2.0, ECLASS XML 3.0 |
| ECLASS 10.0.1 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.0, ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 10.0.1 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 9.1 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V8.0, ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 9.1 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 9.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V7.0, ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 9.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 8.1 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V7.0, ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 8.1 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 8.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V7.0, ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 8.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 2.0 |
| ECLASS 7.1 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V7.0, ECLASS XML 1.0 |
| ECLASS 7.1 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 1.0 |
| ECLASS 7.0 BASIC | ECLASS BASIC CSV V7.0, ECLASS XML 1.0 |
| ECLASS 7.0 ADVANCED | ECLASS XML 1.0 |
| ECLASS 6.2.1 | ECLASS CSV V5.2 |
| ECLASS 6.1 | ECLASS CSV V5.1 |
| ECLASS 6.0.1 | ECLASS CSV V5.0, ECLASS XML 2.0 |
CSV Format
The ECLASS CSV format contains all elements that were already available before Release 7.0: classification classes, keywords, properties, values, units, synonyms and all of their relations. The usual CSV export format of the ECLASS-standard includes eight CSV files, which Office programs such as MS-Excel and MS-Access can process and implement. The ReadMe pages describes the amendments, structure, contents, and relations of the CSV files. For BASIC CSV the character code UTF-8 is set as standard.
XML Format
With effect from ECLASS 7.0, it has also been available as an additional export format in ECLASSXML format for automatic ECLASS standard processing. This export format is based on an ISO-standardised XML format for product data exchange. Related specifications are published in ISO 13584-32 ontoML . These specifications offer a uniform and comparable data structure for communications between machines. Consequently, two export formats are available for processing and implementing Basic Representation. Export of Advanced Representation is only available in ECLASSXML-format. One major difference to the CSV format is that in ECLASSXML, deprecated elements are still included.
Overview of ECLASS XML File Formats
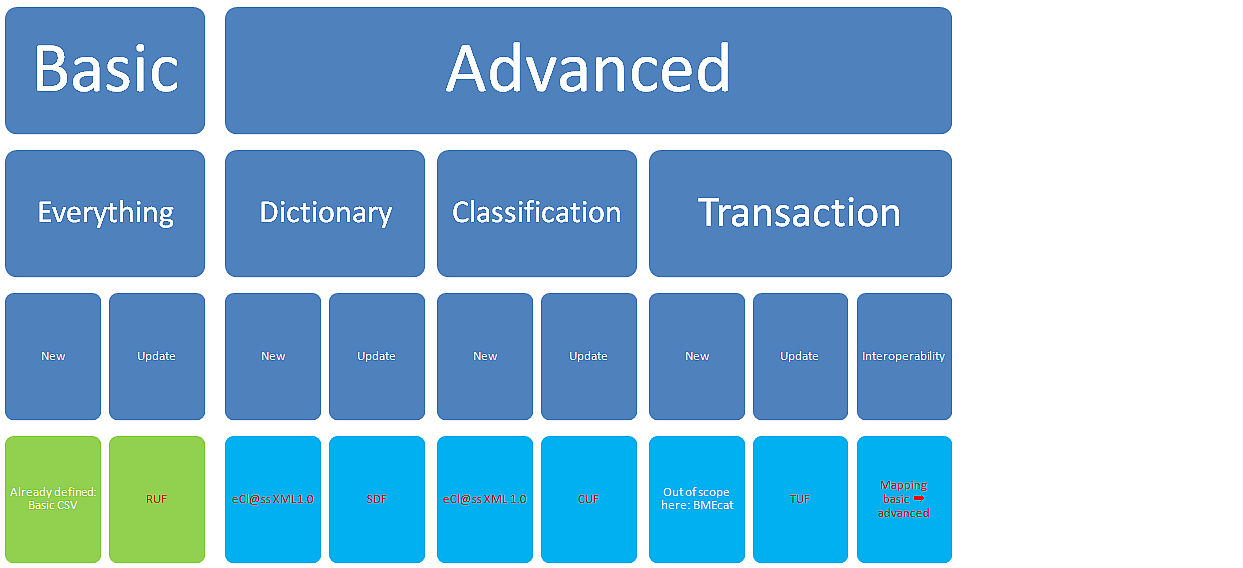
As depicted in Figure 2 there exist copious file formats for basic and advanced users aimed at various types of content (2nd row) and purposes (3rd row).
All formats are whenever possible based on ISO/IEC or other international standards: Only in case no standard format was existing for the given problem, an ECLASS XML schema was developed.
- ISO 13584-32 (“ontoML”)
OntoML is a standardized transformation of the ISO 13584/IEC 61360 data model into an XML representation. It is the core XML Format for exchange of ECLASS product description and classification. OntoML is capable of transporting product descriptions (valuations, i.e. property value pairs as well).
To facilitate this, it uses its complementary ISO 29002 standard.
- ISO 29002
ISO 29002 is an interoperability standard, which provides a repository to be used in various ISO XML formats. It is used in ontoML.
- Genericode
Genericode is a standard model and a XML representation of the content of a code list (also known as enumerations or controlled vocabularies) including data associated with items in a code list. Additionally genericode can provide a standard model and XML representation for how new code lists are derived from existing code lists. This simplifies the effort of understanding how a new code may be represented but also how a new code list version differs from the previous version. Additionally it can simplify the effort in calculating the impact of the change on existing systems and processes.
- UnitsML
UnitsML is a project underway at the (US) National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to develop a schema for encoding scientific units of measure in XML. UnitsML allows encoding of scientific units of measure and quantities into XML and will validate XML documents that use UnitsML. Initial development of this schema was done at NIST, but completion of the development process should include input from the international scientific and engineering community. Towards this end, NIST is initiating an OASIS Technical Committee to address any needed changes in the schema and publish a final recommendation.
Please visit the other pages in this category for a high-level description of the XML formats directed towards advanced users and content.
Functionality matrix
The following matrix provides a functionality overview of both the BASIC and ADVANCED Representations.
| Characteristic | ECLASS 7.0 BASIC | ECLASS 7.0 ADVANCED |
| Basic functionalities | ||
| Hierarchic class structure | × | × |
| IRDI as unique identifier of structural elements | × | × |
| Keywords at class level | × | × |
| One-dimensional property lists for goods/product description | × | - |
| Two-dimensional property lists for a structured goods/product description | - | × |
| Possibility to use value lists | × | × |
| Possibility to use value suggestions | × | × |
| Properties have a standardised structure | × | × |
| Use of aspects | × | |
| Use of property blocks | × | |
| Use of dependent properties | × | |
| Format display for Integer/Real optional | x | x |
| List of alternative units |
| × |
| Units are DIN conformant | × | × |
| Dynamic functionalities |
|
|
| Polymorphism | - | × |
| Cardinality | - | × |
| Data types |
|
|
| Integer Count | × | × |
| Real Count | × | × |
| Integer Measure | × | × |
| Real Measure | × | × |
| String translatable | × | × |
| String non translatable | × | × |
| Boolean | × | × |
| Timestamp | × | × |
| Time | × | × |
| Currency | × | × |
| Level type | × | |
| Axis type | × | |
| Download |
|
|
| CSV | × | |
| ECLASSXML | × | × |
| Update support |
|
|
| Transaction Update File (TUF) | × | |
| Release Update File (RUF) | × | × |
| Languages |
|
|
| German | × | × |
| English | × | × |
| Content |
|
|
| 3 new segments | × | × |
| Harmonised contents of ETIM 4.0 | × | × |
| Harmonised contents of Proficl@ss 4.0 | × | × |
| Harmonised contents of PROLIST NE100 3.2 | × | |
| Harmonised contents of ECLASS | × | × |
| Complete re-structure of segment 34 medical technology | × | × |
Demo Version


ECLASS provides demo versions free of charge. With these demo versions you can get to know and test the ECLASS classification system in a simple way. The following demo versions are available:
- BASIC CSV 7.1: contains the class 19010202 "Notebook" of Release 7.1 and its complete description in both English and German
- XML 8.0: contains the classes 19010202 "Notebook" and 27141120 "Feed-through terminal block" of Release 8.0 and their complete description as both BASIC XML and ADVANCED XML in English and German
With the ECLASS demo, all interested parties get to know the structure and the structural elements of a particular part of the ECLASS classification system. Contents of the demo versions are the product classification of a Notebook and the description with relevant properties and related values in German and English. As for ADVANCED use, the "Feed-through terminal block" is more interesting, it is also added in the XML demo versions. The demo contains both the BASIC XML and the ADVANCED XML files for a direct comparison of what ADVANCED XML can deliver. With this, the user is enabled to test the implementation of the various CSV and XML files within their respective software systems.
Language Versions
ECLASS is available in different language versions. The following types of languages are being distinguished:
Pivot Language
The pivot language is the original language that is the basis for all other translations. For the ECLASS association this is American English (Language Code: en; Country Code: US). ECLASS e.V. will always maintain all structural elements of its standard in this mandatory language updated and in best quality achievable. Translations of the standard to any other language should be done for congruence with and on basis of the pivot language of ECLASS e.V. only.
Main Languages
Main languages of the ECLASS standard are language versions that are permanently supported and financed by ECLASS e.V. to publish and document authorized structural information. For a main language ECLASS e.V. prepares an updated and complete translation of the pivot language with high quality. Current main language of ECLASS e.V. is German (Language Code: de; Country Code: DE).
Other Languages
Renowned business languages may obtain a status as other languages of ECLASS. For such languages ECLASS e.V. is limited to collect third party translations - also fragments - of its standard. ECLASS e.V. therefore will not warrant for translation quality, relevance or completeness. Currently ECLASS e.V. provides support for up to 14 other languages, as listed below: (figure language versions)
Available Language Versions
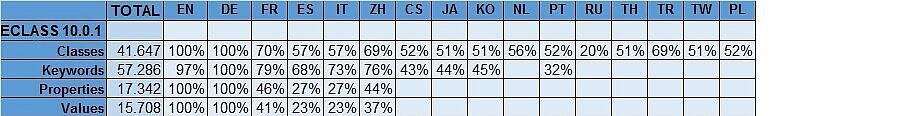
The updated list of all available ECLASS language versions are to be found in the ECLASS Shop.
The overview of all existing languages including their different country variants is to be found in the ISO Language Code.
An example of the degree of translation is the following figure of ECLASS Release 10.0.1:
Deliverables
The deliverables for each release are listed here.
Known Bugs
ECLASS is starting to document all known bugs in any available release. This way, users can have an up-to-date overview on technical errors, as well as mistakes in the content of the ECLASS classification system.
Please have a look at the known bugs page.
Release Update Support
ECLASS e.V. supports standard users with additional information making it possible to update from a directly preceeding ECLASS Release to the following MajorRelease more or less automatically. The result is a significant saving in data processing costs. ECLASS has always published Release Update Files (RUF), but starting with the update from 6.2 to 7.0 ECLASS has made it possible for the first time in a more structured way. Below please find a description of the Release Update File (RUF), Transaction Update Files (TUF), Classification Update File (CUF) and Structure Difference Files (SDF) made available by ECLASS. Release Update File (RUF) are delivered in English and German, whereas Transaction Update Files (TUF), Classification Update File (CUF) and Structure Difference Files (SDF) are language-neutral and therefore delivered in the primary language (English) and are consequently abreviated in 'enUS'. An overview of the update files that are available for the respective releases can be seen in the following table:
| Release | RUF available? | TUF, CUF, SDF available? |
|---|---|---|
| 15.0 to 16.0 | yes | yes |
| 14.0 to 15.0 | yes | yes |
| 13.0 to 14.0 | yes | yes |
| 12.0 to 13.0 | yes | yes |
| 11.x to 12.0 | yes | yes |
| 10.x to 11.x | yes | yes |
| 9.x to 10.x | yes | yes |
| 8.x to 9.x | yes | yes |
| 7.x to 8.x | yes | yes |
| 6.x to 7.x | yes | yes |
| 5.x to 6.x | yes | no |
| 4.x to 5.x | yes | no |
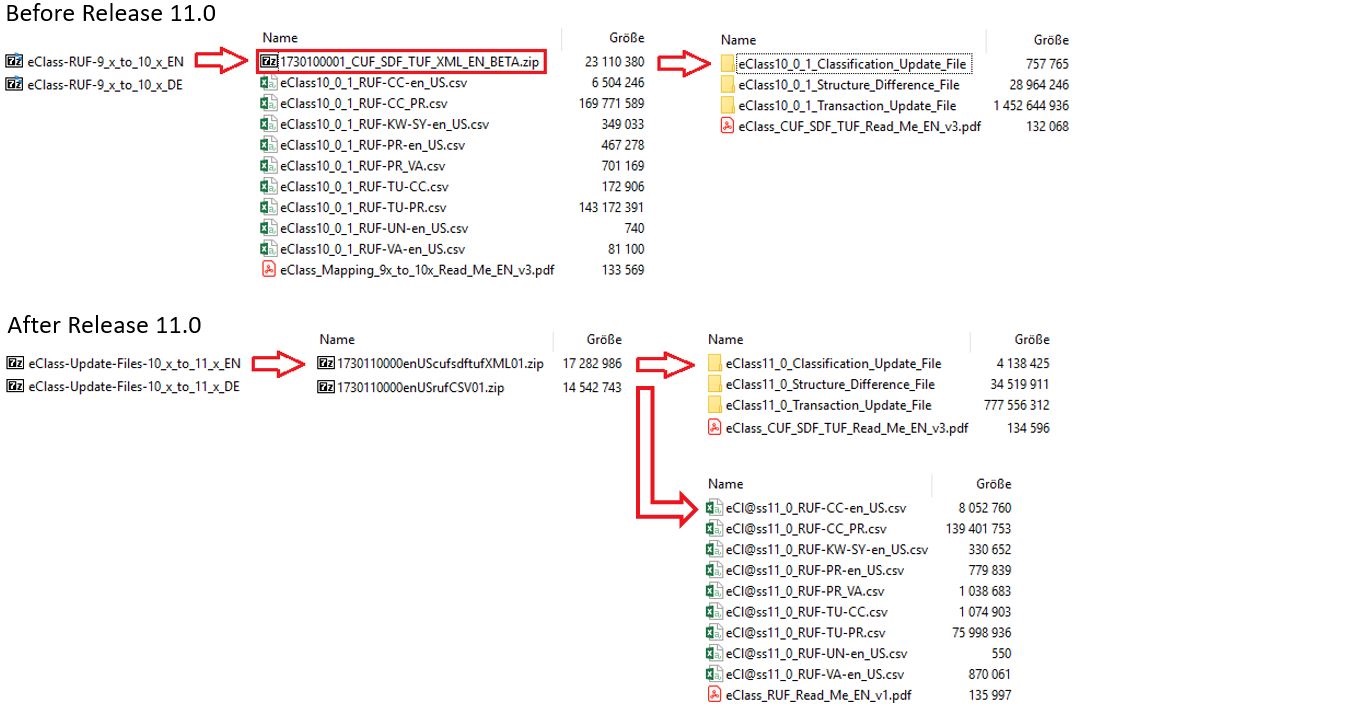
Starting from Release 11.0 the former expressions Mapping Files/Mapping Tables have been changed appropriately into Update-Files, because since these files are used to update from a previous Major or Minor Release to a Major Release. Conversely, Mapping-tables or -files are defined as mapping information between two data-standards (e.g. ETIM to ECLASS or vice versa). Release 11.0 further restructured the delivery of the files from one Zip-file with the name-suffix RUF (contains RUF tables as CSV data but also another Zip-file containing TUF, CUF and SDF Tables as XML data) towards one Zip file which contains now two separate ZIP-Files, distincted between CSV (RUF) and XML (CUF, SDF, TUF) data (see Example 1).
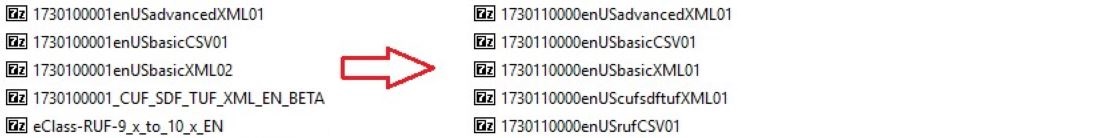
Starting from ECLASS Release 11.0 also, the naming of the Zip-files was aligned with the official naming rules of ECLASS, analogue to all other Release Deliverables. In Example 2 on the left hand side the old naming is visible, whereas on the right hand side, the new naming can be viewed.
Release Update File (RUF)
The Release Update File (RUF), available in CSV format, contain information with regard to release changes made in respect of classes and properties. MOVE/SPLIT/JOIN as well as previous and successive associations are retraceable by means of these files. The RUF are available for ordinary members free-of-charge, any other user can purchase them in the ECLASS Shop.
Transaction Update File (TUF)
The Transaction Update File, abbreviated TUF, made available in XML-format, provide information as to whether previous properties are still valid when using successive properties. This allows a (partly) automatic update of evaluated data files. The first TUF have been made available for the upgrade from 6.2 to 7.0.
Classification Update File (CUF)
The main purpose of the Classification Update File (CUF) is to update classification relations for already classified products, if the classification structure has changed. This can be done by semi-automated update process that uses TUF from a previous ECLASS release to a later ECLASS release (BASIC and ADVANCED versions, XML). TUF contains the results of the changes to the classification by MOVE, SPLIT and JOIN operations, but it does not contain information about new and deleted classes.
Structure Difference File (SDF)
The main purpose of the Structure Difference File (SDF) is to update from one ECLASS release to its subsequent release, if these cannot be kept parallel for technical or business reasons. It is recommended to keep different dictionary releases parallel. If dictionary releases are kept in parallel, the SDF become more obsolete. SDF is an XML genericode list for BASIC and ADVANCED of all those identifiers that were changed in a certain dictionary release. SDF shows all elements that have changed or have been added on element level (like class, property, value etc.) information on the relations is not included.
References
Related Information
- Advanced XML
- Basic CSV
- Basic XML
- Classification Update File
- CSV file description
- Deliverables
- ECLASS-Update
- Known Bugs
- List advanced xml files
- List basic xml files
- List of basic sets of properties
- read me
- Release Update File (RUF)
- Structure Difference File
- Transaction Update File
- Update File CSV
- Update File XML